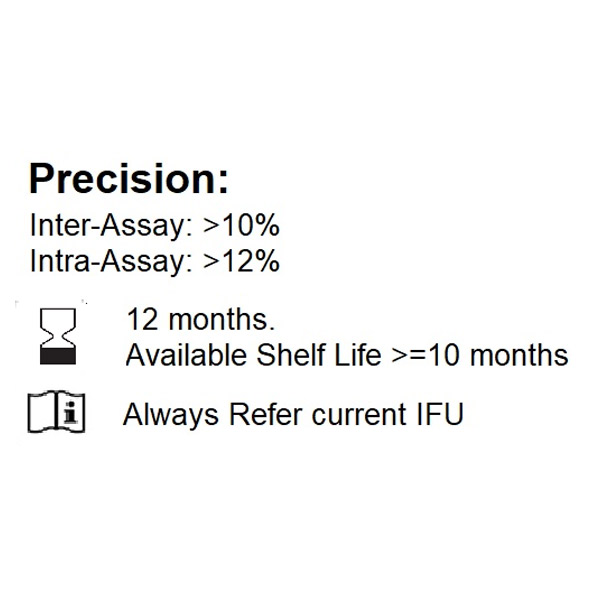
Introduction: ds-DNA is used for the semi-quantitative determination of autoantibodies to nuclear and cytoplasmic antigens in human serum and plasma. Connective tissue diseases (CTD) are a group of autoimmune disorders which are characterized by presence of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) in the blood of patients. ANA are a specific class of autoantibodies that have the capability of binding and destroying certain structures within the nucleus of the cells. Although lower amounts of these antibodies can be seen in the normal population as well, a spurt in titers is seen in patients of CTD. These antibodies are involved in the disease pathogenesis and also constitute the basis for diagnosis and treatment of CTD. ANA have been categorized in two groups: ?Auto-antibodies to DNA (these include antibodies against single and double-stranded DNA (ssDNA, dsDNA)) and histone; ?Autoantibodies to extractable nuclear antigens (ENA). Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a severe disease that involves dysregulation of the immune system, excessive production of pathogenic autoantibodies (and their upregulation in serum), and multiple immunesystem-mediated injuries. Significant levels of anti-dsDNA and anti-ssDNA antibodies are considered to be confirmatory in diagnosis of SLE. The symptoms usually observed are muscle pain, swelling, stiffness