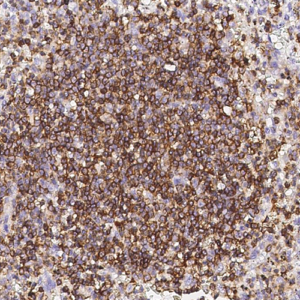
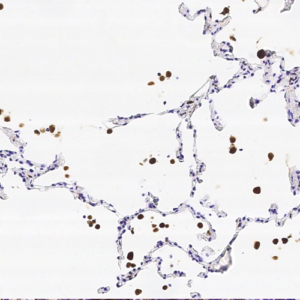
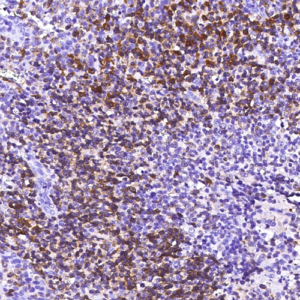
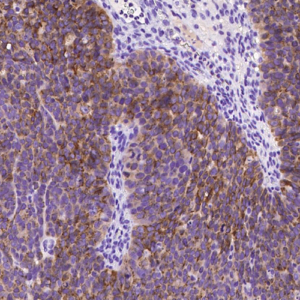
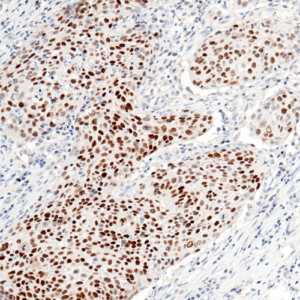
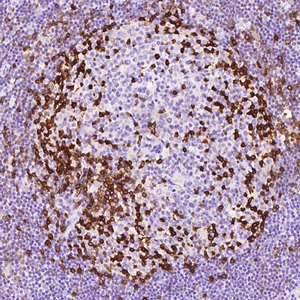
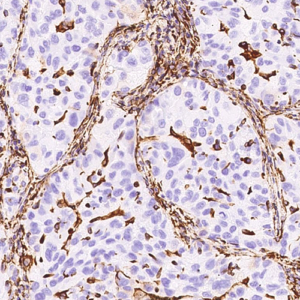
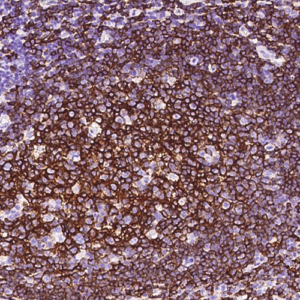
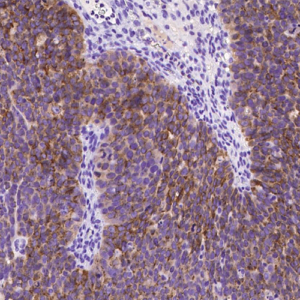
Tumor protein p63 is a protein also known as transformation-related protein 63, TP63, and p63. Tumor protein p63 / p63 is a member of the p53 family of transcription factors whose members P53, p63, and p73 have similar features in their gene structures and functions. An animal model, p63-/- mice has been useful in difining the role p63 plays in the development and maintenance of stratified epithelial tissues. This p63 encoding protein p63 has a dramatic impact on replenishment of cutaneous epithelial stem cells and on ovarian germ cell survival. Although these two fundamental roles of p63 attest to its powerful place in development, its other functions, specifically the apparent capacity of p63, is to supervise the emergence of new cell populations in the breast, prostate, cervix, and upper reproductive tract. P63-/- mice have several development defects which include the lack of limbs and other tissues, such as teeth and mammary glands, which develop as a result of interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium. Mutations in this protein are associated with ectodermal dysplasia, and cleft lip / palate syndrome 3, ADULT syndrome (acro-dermato-ungual-lacrimal-tooth), limb-mammary syndrome, et al.
SKU: KPIH10208
P63
The P63 gene is a member of the P53 gene family and encodes at least six main same species with transactivation, death-induced activity and dominant inactivation activity. The P63 protein is expressed in a variety of normal tissues in humans and mice, including proliferating epithelial cells, cervix, urothelium and prostate.
| Pack Size | 100 ul |
|---|---|
| Source | Rabbit |
| Clone | 143 |
| Class | IgG |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Tested Reactivity | Human p63 |
| Localization | Nucleus |
| Pretreatment | Thermal Remediation |
| Applicable Tissue | Paraffin Section |
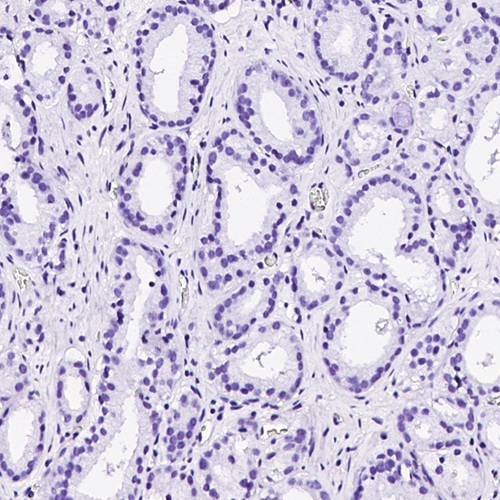
| Positive Control | Human prostate |
| Storage Temperature | Store at -20 Degrees |