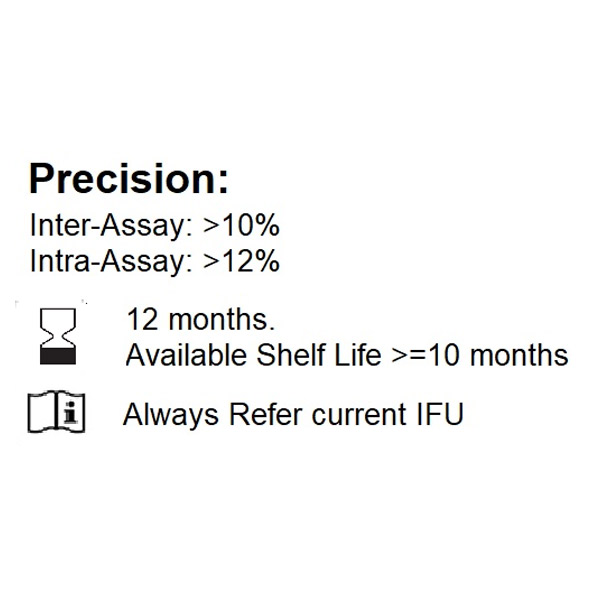
Introduction: Testosterone is a steroid hormone belonging to an androgen group. It is the principal male sex hormone and the “original” anabolic steroid. It is derived from cholesterol. The largest amounts of testosterone are synthesized by testes, but is also synthesized in smaller quantities by the theca cells of the ovaries, the zona reticulosa of the adrenal cortex, and the placenta. Substantial amounts of the testosterone in women are also produced from estradiol by reverse aromatization in the liver, adipose cells, and other peripheral tissues. The mechanism includes: by activation of the androgen receptor (directly or as DHT), and by conversion to estradiol and activation of certain estrogen receptors. Testosterone Free is transported into the cytoplasm of target tissue cells, where it can bind to the androgen receptor, or can be reduced to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by the cytoplasmic enzyme. It plays a major role in maintaining the secondary sexual characteristics in males, which are considered as virilizing effect; whereas anabolic effects include growth of muscle mass and strength, increased bone density and strength, etc.