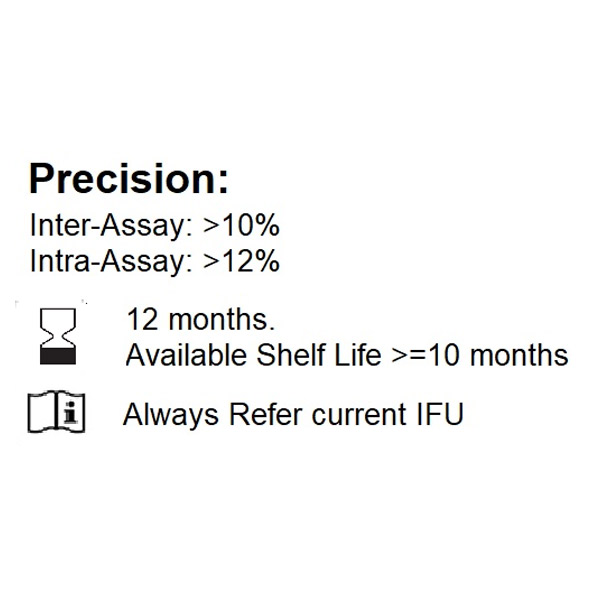
Introduction: Celiac disease (CoD) also known as sprue, non-tropical sprue, gluten-sensitive enteropathy, defined as an autoimmune disorder originating by an aberrant adaptive immune response against gluten-containing grains in susceptible individuals. In celiac subjects the ingestion of gluten leads to an enteropathy with an impairment of the mucosal surface and, consequently, abnormal absorption of nutrients.. The active phase of CoD is accompanied by elevated levels in serum of immunoglobulin A (IgA) autoantibodies against endomysium (IgAEmA) and tissue transglutaminase (IgA-tTG). Antigliadin antibodies (AGAs) are antibodies of the IgA and IgG classes found in the sera of celiac disease patients. These antibodies mainly target gliadin-derived peptides, which are the main proteins of gluten. The symptoms usually observed are tooth discoloration or loss of enamel, pale sores inside the mouth, irregular menstrual periods, infertility and miscarriage, dermatitis herpetiformis